Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has emerged as the most critical global crisis of the 21st century. COVID-19 cases have exceeded 30 million as of September 28, 2020 (1). A number of studies have indicated an increase in anxiety, depression, and other psychopathologies during the COVID-19 pandemic (2–7). Such disturbances have occurred, in particular, in individuals with previous history of psychological illness, who have also been found to be at increased risk of contracting COVID-19 (8). Furthermore, worsening of psychiatric conditions has also been associated with higher risk of suicidal ideation (9, 10).
Psychiatric conditions constitute a significant burden on healthcare systems and economy (4, 11–13). The COVID-19 pandemic has given rise to even greater challenges for an already struggling system of mental health care. Moreover, it has been associated with an increase in use of mental health and suicide prevention helplines (14). Furthermore, new methods of psychological/psychiatric care delivery through telemedicine are being increasingly adopted (15). It is paramount for the optimization of mental healthcare delivery during these challenging times that the most vulnerable populations are efficiently identified.
To address this, we analyzed the data from participants with preexisting psychiatric conditions from our global study on the mental health impact of COVID-19 (10). Each patient report of worsening of psychiatric conditions was then cross-analyzed with participants' demographics, opinions/outlooks, personality traits, current household conditions, previous history, and other factors associated with COVID-19 to identify risk and resilience factors for worsening psychiatric condition. The results were then verified in an independent clinical cohort of psychiatric patients that consulted a psychiatry practice in Houston, TX, USA, during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
Study Design
The study comprised two independent evaluations: (1) a cross-sectional electronic survey-based assessment of individuals older than 18 years willing to participate in the study and (2) evaluation of anonymized clinical records of psychiatric patients older than 18 years.
Online Survey
The anonymous online survey was conducted among participants from diverse demographic groups to examine the status of their preexisting psychiatric conditions that were verified via standardized self-report scales for general psychological disturbance, risk for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), symptoms of depression, and suicidal ideation. The survey was available online for a period of 15 consecutive days beginning 18:00 Central European Time on March 29, 2020, and concluding on 18:00 Central European Time on April 14, 2020.
The questionnaire was developed through close consultation between a neuroscientist, a neuropsychologist, a psychiatrist, a data scientist, and a psychiatry clinic manager. The questionnaire included closed-ended questions that assessed participant characteristics and opinions and screened for neuropsychiatric symptoms through standardized and validated self-report scales. The questionnaire prototype was prepared in English (Appendix 1) and translated into 10 additional languages (Arabic, Bosnian, French, German, Greek, Italian, Persian, Polish, Spanish, and Turkish; Appendix 2). The translation was performed by bilingual native speakers and vetted by volunteers native to those countries. The feasibility of each questionnaire was confirmed using pilot studies that comprised 10 participants each. These responses were excluded from the final analysis.
The questionnaires (Appendix 1) included a section on participant demographics (age, gender, country, residential setting, educational status, current employment status), household conditions (working/studying from home, home isolation conditions, pet ownership, level of social contact, social media usage, time spent exercising), COVID-19–related factors (knowing a coworker, friend, or family member who tested positive for or demised due to COVID-19; prediction about pandemic resolution), personality traits (level of optimism, level of extroversion), previous history of psychiatric disease and/or trauma, previous exposure to human crisis, and level of satisfaction with actions of the state and employer during the current crisis. All questionnaires were rated on binary (yes/no) responses or Likert-type scales.
The other sections contained general health assessment based on World Health Organization (WHO) Self-Reporting Questionnaire-20 (SRQ), Impact of Event Scale (IES), and Beck's Depression Inventory II (BDI) (16–18). These scales were chosen based on their usage and efficacy in previously employed works studying the psychological impact of human crises such as the severe acute respiratory syndrome epidemic (19–27). IES wording was purposefully adjusted to assess the impact of an ongoing event rather than a past event.
Using a nonrandomized referral sampling (snowball sampling) method, participants were contacted by a team of 70 members (study authors and volunteers who have been acknowledged in the Acknowledgments) using electronic communication channels including posts on social media platforms, direct digital messaging, and personal and professional email lists. For the survey, 12 countries were included in the “featured” list. These countries included United States, Spain, Italy, France, Germany, Iran, Turkey, Switzerland, Canada, Poland, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Pakistan. The data collection procedures were repeated at least thrice during the data collection period (March 29–April 14, 2020).
An overall total of 13,332 responses were collected. Surveys were excluded if they were completed by participants who were younger than 18 years (n = 34), were missing responses for all dependent variables (n = 112), had been submitted previously (n = 325), were missing geographic location (n = 20), or were from WHO AFRO region (n = 24). When the responses were missing for individual items, the missing data were considered null and excluded from the analysis for that particular variable. In this follow-up study, however, only responses from participants who reported suffering from a previous psychiatric condition (n = 2,734) were considered valid.
Clinical Study
The clinical data were extracted and analyzed for all the adult patients who consulted for online follow-up clinical evaluations at a psychiatric care facility (Texas Behavioral Health) based in Houston, TX, USA, during March 29–April 14, 2020. The inclusion criteria were previous diagnosis of major depressive disorder or anxiety disorders (generalized anxiety disorder and PTSD). Patients with diagnoses other than these and those younger than 18 years were excluded. Only the data from patients consenting to use of their records for this research were included in the study.
Clinical data for each patient were examined by clinic assistants blinded to the study design. The following information was extracted: age, gender, home-isolation status during COVID-19, social support during COVID-19, past exposure to trauma or a human crisis situation, and clinical diagnosis. Worsening of psychiatric conditions was assessed based on clinician report of new symptoms, need to increase or adjust the medication, and referral for a new therapy.
Data from 318 patients were considered valid for analysis. When the responses were missing for individual items, the missing data were considered null and excluded from the analysis for that particular variable.
Ethical Considerations
Informed consent was obtained from each survey and clinical participant to allow anonymous recording, analysis, and publication of their answers. The data were collected in a completely anonymous fashion without recording any personal identifiers, and the confidentiality of the participants was maintained throughout all phases of the study. The study procedures were reviewed and approved by the University of Zurich Research Office for Scientific Integrity and Cantonal Ethics Commission for the canton of Zurich (Switzerland), BRAINCITY, Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, Warsaw (Poland), and the Faculty of Medicine, University of Tuzla, Tuzla (Bosnia and Herzegovina).
Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using R version v.3.6.3 and Rstudio (28). All figures were produced using the packages ggplot2 (29) and CGPfunctions (30)
Unadjusted analysis for worsening of psychiatric conditions in both the survey and the clinical cohort involved Fisher exact test. For the survey, the categorical predictors included gender, residential status, education level, employment status, being a medical professional, working remotely from home, satisfaction with employer, satisfaction with the state (government), home-isolation status, interaction with family and friends, social media usage, ability to share concerns with a mental health professional, ability to share concerns with family and friends, prior exposure to a human crisis situation, previous exposure to trauma, level of extroversion, prediction about COVID-19 resolution, and one's self-determined role in the pandemic. For the clinical study, the categorical predictors included age, gender, home isolation status, and social support during home isolation.
Multiple logistic regression models were built to generate odds ratios (ORs) for worsening of psychiatric conditions both in the survey and the clinical cohorts. All statistical analyses were performed by the analysis team comprising MP, SG, PR, and AJ in consultation with ZB.
Results
Survey Study
Demographics
A total of 2,734 responses were considered valid with the highest responses from the United States (874), Poland (255), Canada (246), Spain (205), and Pakistan (203). The distribution of the responses across the 12 featured countries and the WHO regions is presented in Supplementary Item 1. Canada had the highest (80.89%) proportion of patients reporting worsening of their psychiatric condition followed by Pakistan (72.41%) and the United States (67.5%). Turkey had the lowest percentage (28.57%) for worsening of psychiatric conditions (Figure 1).
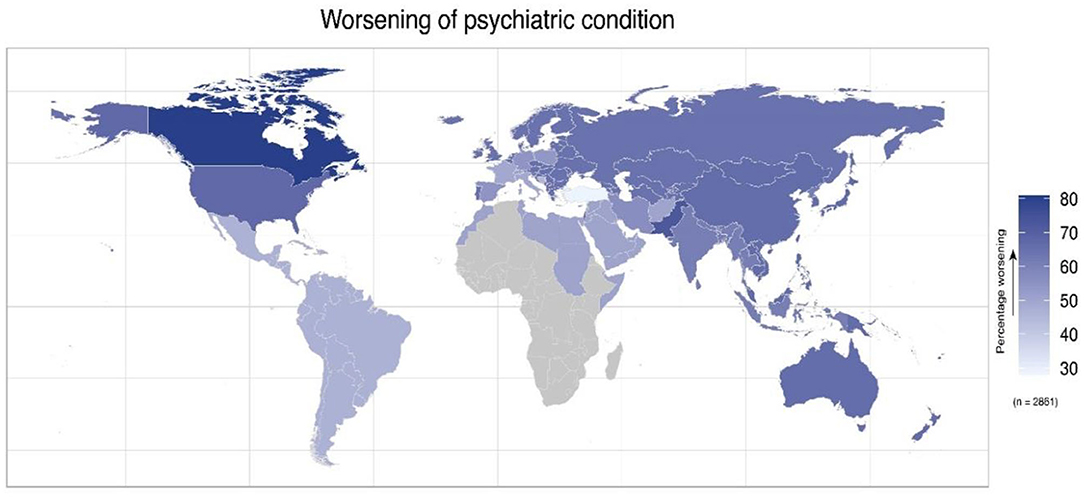
Figure 1. Geodemographic representation of the survey participants with preexisting psychiatric condition that reported worsening of their condition. The map shows the percentage of worsening preexisting psychiatric conditions separately for each of the featured countries and for each of WHO regions.
There was a disproportion in valid responses, with higher numbers from those participants who were female (79.44%); residing in urban areas (84.6%); with advanced educational qualification, i.e., bachelor's degree or higher (71.5%); working/studying remotely from home (65%); and currently under home isolation with a partner/family (82.77%). Also notable were responses expressing some level of satisfaction with COVID-19–related employer (52.67%) and state response (64.26%) and spending <15 min on daily physical exercise (52.99%). A majority of participants also reported increased social media usage (65.42%), less-than-usual or minimal interaction with family and friends (64.88%), and feeling some level of control in protecting themselves and others during the COVID-19 pandemic (94.36%).
Participants' report of worsening of psychiatric conditions was verified by comparing the SRQ, IES, and BDI scores between patients reporting worsening of psychiatric conditioning vs. those reporting no change. All scores were significantly (p < 0.05) higher in patients reporting worsening of psychiatric conditions. Distribution of patients reporting no change in their condition in comparison to worsening along the SRQ, IES, and BDI scales further confirmed this pattern (Figure 2).
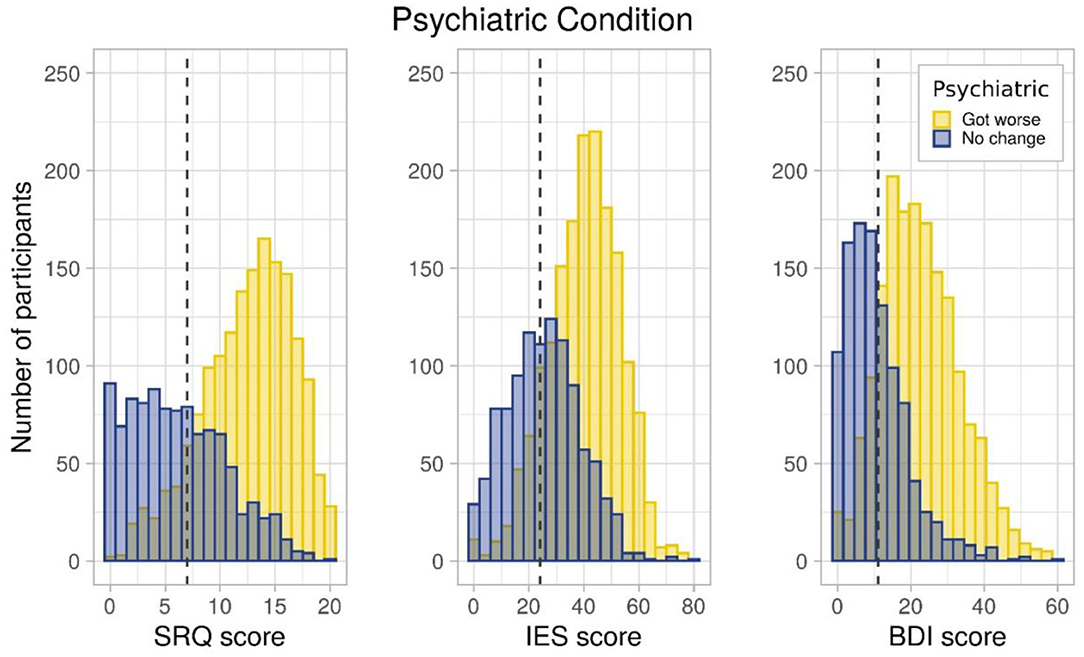
Figure 2. Population distribution of people with preexisting psychiatric condition across SRQ, IES, and BDI score.
Unadjusted Analysis of the Worsening of Psychiatric Condition
Unadjusted χ2 analysis of association between different patient factors and their report of psychiatric condition worsening revealed significantly higher reports of worsening in women, patients with advanced education, patients who reported being home isolated, and those with previous trauma exposure. Moreover, patients reporting dissatisfaction with the response of their government and employer during COVID-19 were more likely to report worsening of psychiatric condition. Finally, patients who identified themselves as a pessimist, felt lack of control during the current situation, and had negative prediction about COVID-19 resolution were more likely to report worsening of their psychiatric condition.
On the contrary, patients who were able to interact and share concerns with their family and friends or with a health professional like usual during COVID-19 were less like to report worsening of their preexisting psychiatric conditions. The details of the unadjusted categorical analysis are present in Table 1.
Adjusted Analysis of the Worsening of the Psychiatric Condition
Adjusted analysis was then performed for patients' report of psychiatric condition worsening via logistic regression to adjust for confounding associations. Report of feeling no control over the situation during the COVID-19 pandemic showed an 89% increase in the odds of reporting worsening of psychiatric condition (OR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.18–3.03). Similarly, no or minimal social interaction during COVID-19 was associated with higher odds of reporting worsening of the psychiatric condition during COVID-19 (OR, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.30–1.87). Not being satisfied with the government's response also showed an increased probability of worsening of psychiatric condition during COVID-19 (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.09–1.58). Finally, female psychiatric patients were more likely to report worsening of their psychiatric condition compared to male patients (OR, 1.70; 95% CI, 1.28–2.00; Figure 3).
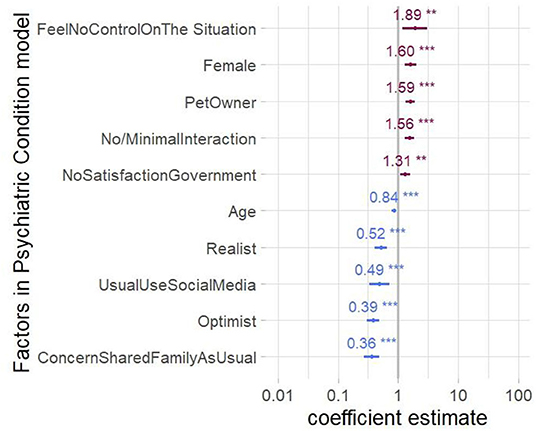
Figure 3. Factors associated with psychiatric condition worsening. Foster plot shows the mean estimates and the 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for adjusted coefficients significantly affecting the reported worsening of psychiatric condition by the patients. Factors indicating more odds of worsening are shown in red, whereas factors indicating less odds of worsening are in blue.
On the contrary, the ability to share concerns with family and friends like usual and optimistic attitude decreased the worsening of the psychiatric condition [OR, 0.39 (95% CI, 0.30–0.49) and OR, 0.36 (95% CI, 0.27–0.49)]. Furthermore, as-usual usage of social media during COVID-19 and considering oneself a realist also decreased the probability of worsening of psychiatric condition [OR, 0.49 (95% CI, 0.34–0.71) and 0.52 (95% CI, 0.41–0.65)].
Clinical Study
The valid clinical samples comprised 71.58% females, and the diagnosis of a vast majority (83.56%) of patients was major depressive disorder. Clinicians identified new symptoms in 44% of patients, with sleep disturbance being the most common emerging symptom. Collectively, clinicians felt the need to make treatment adjustments in almost half of the patients in the form of starting a new medication or treatment modality or adjusting the dose of a currently prescribed medication (Supplementary Item 3).
Among the patient-related factors, female gender significantly increased the likelihood of a change of medication by the clinician (OR, 2.22; 95% CI, 1.03–4.49). However, other patient-related factors such as age and level of social support during home isolation were not associated with any clinical intervention (Table 2).
Discussion
This study highlights a significant impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on psychiatric patients worldwide. At least 50% of the psychiatric patients evaluated in this study from 8 of the 12 featured countries reported worsening of psychiatric conditions. Notably, the self-reported worsening of psychiatric conditions was cross-validated with patients' scores on scales assessing general psychological disturbance, risk of PTSD, and depression. Severity of psychopathology assessed through these scales confirmed the patients' report of psychiatric condition worsening. Finally, clinician reports from an independent cohort of psychiatric patients in the United States confirmed that almost half of the patients reported new symptoms and required treatment adjustments during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In addition to ascertaining if there has been a general worsening of psychiatric conditions during COVID-19, a major aim of this study was to identify risk factors for such worsening. Female gender, having no or minimal interaction with family and friends, not being satisfied with the actions of the government, and feeling lack of control over the situation were associated with worsening of psychiatric conditions in the survey cohort. Patients who were older, considered themselves optimists or realists, used social media like usual, and were able share their concerns with family and friends during COVID-19 like usual were less likely to report worsening of psychiatric conditions. Notably, examination of the clinical cohort confirmed some of these findings. Clinicians reported significantly higher adjustment of medications for female psychiatric patients.
The results of this study confirm previous speculations and concerns about the vulnerability of psychiatric patients during the COVID-19 crisis (7, 31). Compared with previous studies on the impact of mental health during pandemic, this study focuses on the deterioration of psychiatric illnesses in response to COVID-19. Other studies have focused on vulnerable populations including indigenous, migrant, and imprisoned populations; people with disabilities; women (32); frontline workers (33); and the elderly (11), but thus far has not included populations with preexisting psychiatric illnesses. Tracing the worsening of psychiatric illnesses in response to COVID-19 can provide the insight necessary to improve mental health systems. Moreover, keeping the vulnerability of those with preexisting psychiatric illness in mind, health systems can become better equipped to address the concerns of this population, mitigate the risk of further mental deterioration, and reduce prevalence of suicidal ideation. Previous studies have reported the importance of adequate procedures to detect early mental health worsening (34), but have scarcely been conducted in the context of pandemics such as COVID-19.
Identifying factors that are associated with worsening of psychiatric conditions has important implications for psychiatric prognostics and therapeutics. In our previous study, patients with prior psychiatric disease reported increased suicidal ideation (10). Understanding factors associated with psychiatric disease during a pandemic can help the patients, their family, and caregivers to screen and identify those at an increased risk of mental health crisis situations such as suicide attempts. Factors identified in this study including gender-based factors and prior exposure to trauma warrant further investigation to ensure that health systems can provide for the needs of a vulnerable population.
Previous research also shows increased gender-based disparity in association with humanitarian crises (35). During the Ebola outbreak of 2014–2016, women were reported to be at an increased risk of abuse, violence, and a lack of access to protective instructions (32). Moreover, women are more susceptible to the effects of economic insecurity, social isolation, disaster-related unrest, reduced health service accessibility, inability to escape abusive partners, and violence against healthcare workers. Measures such as social isolation have increased women's exposure to domestic violence: early reports from a police station in China's Hubei Province revealed three-times increased domestic violence targeting women during the COVID-19 quarantine period of February 2020 (32).
There are several strengths of our global and immediate approach to the examination of the vulnerable population of psychiatric patients during COVID-19. First, the sample size is large. Second, to reduce the participation bias, the study was administered in 11 different languages, ensuring generalizability across countries and cultures. Participants from the 12 countries represented a diverse perspective according to the economic structure and government support provided by their respective countries. For instance, countries such as Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Switzerland, and United States are classified as high-income economies according to the World Bank Atlas, whereas Bosnia and Herzegovina, Iran, Pakistan, and Turkey are considered middle- or lower-income countries (36). Third, as one of the earliest examinations of the mental health impact of COVID-19, our study carries the unique strength of immediate data collection during the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic in North America and Europe. In both the online survey and the clinical design, the psychiatric conditions were present in the patients at the baseline and thus indicate the potential effect of the pandemic on worsening of these conditions. Finally, the objective assessment of worsening of psychiatric conditions by the clinicians in the independent clinical cohort is an important contribution and strength of this study.
This study also has potential limitations that warrant consideration while interpreting the results. First, the sampling method is nonrandomized for the survey cohort. While a nonrandomized approach has potential disadvantages, we hope that the results of this study can nonetheless serve as a resource and catalyst for further investigation. For a similar global or continent-wide study, entities such as the WHO and the EU (European Union) could develop and administer a similar study with a wider reach. Second, the data were exclusively collected online for the survey—this may have excluded those less well-versed in web usage such as underdeveloped, rural, or disadvantaged populations. Nevertheless, to counter existing language barriers that may compound computer illiteracy, we translated the survey in native and official languages for each of the featured countries. Another important consideration is a potential confounding effect of other important factors, such as duration and severity of preexisting psychiatric conditions that may influence the impact of the current stressful events (37). Furthermore, quality of mental health services and mental health literacy could play an important role in mediating or modulating the effects of the pandemic on neuropsychiatric functioning of patients. Indeed, this could explain the regional differences in patient reports of psychiatric condition worsening. Lastly, a longitudinal assessment of the evolution of psychological symptoms in response to the COVID-19 pandemic is imperative and is the subject of an ongoing investigation by our group.
In conclusion, this effort highlights a significant impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the mental health of psychiatric patients and elucidates prominent associations with their demographics, household conditions, personality traits, and attitude toward COVID-19. These results could serve to inform mental health professionals and policymakers across the globe, aiding in dynamic optimization of mental health services during and following the COVID-19 pandemic, and reducing its long-term morbidity and mortality.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: All data presented in the main and Supplementary Items are deposited on the repository below and are available for verification upon request. https://osf.io/3vupe/?view_only=80f71b6f0c8d49b08573ea12eab10d33.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Zurich Cantonal Ethics Commission, Zurich, Switzerland Medical Faculty of the University of Tuzla, Tuzla, Bosnia Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, Warsaw, Poland. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
SG and MP contributed in conceptualization, questionnaire development, data collection, data mining, data analysis, visualization, review, and editing. ZA contributed in data collection, manuscript writing, review, and editing. BS, SL, KA, AD, AB, LH, SE, HJ, LR-P, VW, AAl, MB, and DS contributed in questionnaire translation, data collection, data mining, review, editing, and project co-ordination. PR contributed in data analysis and visualization. RN contributed in data collection, manuscript writing, review, and editing. ZB-T contributed in data analysis. ZH, AAr, and SQ contributed in clinical data collection and project co-ordination. AJ contributed in conceptualization, questionnaire development, study approval, data collection, data analysis, data visualization, manuscript writing, review, editing, project administration, and supervision. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
AJ is supported by an International Research Agenda (MAB) grant by Foundation for Polish Science (FNP).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the contribution of Luciana Armengol (Argentina), Prof. Anthony Hannan, Maxine Mason, Qi Hui Poh (Australia), Taria Brkić (Bosnia and Herzegovina), Barbara Levinsky (Brazil), Alexandra Schimmel and Lea Caya-Bissonnette (Canada), Claudia Valenzuela Rios (Chile), Marc Scherlinger, Alice Tondre, Lola Kouroma, and Morgane Roth (France), Katharina Schlerka, Lisa Garrelts, and Romy Seifert (Germany), Lena Heck (Germany/Switzerland), Varsha Hooda, Deepak Tanwar, and Chakradhar Yakkala (India), Prof. Mohammad Es haghi and Sepehr Namirad (Iran), Darren Kelly (Ireland), Nour Mosawy (Jordan), Dayra Lorenzo (Mexico), Chirine Katrib (Lebanon/France), Usman Mukhtar, Uzair Jaswal, and Mubaris Bashir (Pakistan), Prof. Kornelia Kedziora-Kornatowska, Milena Czarnocka and Juli Davis (Poland), Ana Alexandra Moraru (Romania), Shoaib Jawaid (Saudi Arabia/United Arab Emirates), Myriam Merarchi (Singapore/France), Michelle McLuckie, Doman Obrist, Niharika Gaur and Graciela Huber (Switzerland), Aurelia Muller (Taiwan/Germany/Switzerland), Burak Ozan (Turkey), Carmen Neagoe and Aleena Malik (UK), Anastasiia Timmer (Netherlands/United States), Colette Rausch, Prof. Paul Schulz, Prof. Mo Salman, Saleha Tahir, Laura Luebbert, Sarish Khan, Rebecca Sager, Lupita Lozano, and American Physician Scientist Association (United States) for their dedicated help in data collection. We are also thankful to Lena Heck and Giuseppe Parente (University of Zurich) for technical support. Finally, we would like to express our gratitude to Prof. Selmira Brkić (Faculty of Medicine, University of Tuzla, Bosnia and Herzegovina), Prof. Leszek Kaczmarek (Director, Nencki-EMBL Braincity, Warsaw, Poland), University of Zurich Research Office, Zurich Cantonal Ethics Commission, Texas Behavioral Health, and European MD-PhD Association for their expedited review of the study procedures under extra-ordinary circumstances and for their organizational support. This manuscript has been released as a pre-print at Medrxiv (38).
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.581426/full#supplementary-material
References
2. Cosić K, Popović S, Šarlija M, KesedŽić I. Impact of human disasters and COVID-19 pandemic on mental health: potential of digital psychiatry. Psychiatr Danub. (2020) 32:25–31. doi: 10.24869/psyd.2020.25
3. Lee J. Mental health effects of school closures during COVID-19. Lancet Child Adolesc Heal. (2020) 4:421. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30109-7
4. Thome J, Coogan A, Fischer M, Tucha O, Faltraco F. Challenges for mental health services during the 2020 Covid-19 outbreak in Germany. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. (2020) 74:407. doi: 10.1111/pcn.13019
5. Kar SK, Arafat SY, Sharma P, Dixit A, Marthoenis M, Kabir R. COVID-19 pandemic and addiction: current problems and future concerns. Asian J Psychiatr. (2020) 51:102064. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2020.102064
6. Galea S, Merchant RM, Lurie N. The mental health consequences of COVID-19 and physical distancing: the need for prevention and early intervention. JAMA Intern Med. (2020) 180:817–8. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.1562
7. Correa H, Malloy-Diniz LF, da Silva AG. Why psychiatric treatment must not be neglected during the COVID-19 pandemic. Braz J Psychiatry. (2020) 42:449. doi: 10.1590/1516-4446-2020-0995
8. Yao H, Chen J-H, Xu Y-F. Patients with mental health disorders in the COVID-19 epidemic. Lancet Psychiatry. (2020) 7:e21. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30090-0
9. Gunnell D, Appleby L, Arensman E, Hawton K, John A, Kapur N, et al. Suicide risk and prevention during the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Psychiatry. (2020) 7:468–71. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30171-1
10. Plomecka MB, Gobbi S, Neckels R, Radziński P, Skórko B, Lazerri S, et al. Mental health impact of COVID-19: a global study of risk and resilience factors. PsyArXiv [Preprint]. (2020). doi: 10.1101/2020.05.05.20092023
11. Mesa Vieira C, Franco OH, Gómez Restrepo C, Abel T. COVID-19: the forgotten priorities of the pandemic. Maturitas. (2020) 136:38–41. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.04.004
12. De Girolamo G, Cerveri G, Clerici M, Monzani E, Spinogatti F, Starace F, et al. Mental health in the coronavirus disease 2019 emergency-The Italian Response. JAMA Psychiatry. (2020) 77:974–6. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.1276
13. Kar SK, Yasir Arafat SM, Kabir R, Sharma P, Saxena SK. Coping with mental health challenges during COVID-19 BT. In: Saxena SK, editor. Coronovirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapeutics. Singapore: Springer (2020). p. 199–213.
14. Tan R. In an Era of Quarantine, Crisis Hotlines Face Growing – and Urgent – Demand. Washington, DC (2020).
15. Calton B, Abedini N, Fratkin M. Telemedicine in the time of coronavirus. J Pain Symptom Manage. (2020) 60:e12–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2020.03.019
16. Sartorius N, Janca A. Psychiatric assessment instruments developed by the World Health Organization. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. (1996) 31:55–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-80202-7_12
17. Weiss D, Marmar C. The impact of event scale–revised. In: Wilson J, Keane T, editors. Assessing Psychological Trauma and PTSD. New York, NY: Guildfor (1997).
18. Upton J. Beck depression inventory (BDI). In: Gellman MD, Turner JR, editors. Encyclopedia of Behavioral Medicine. New York, NY: Springer (2013). p. 178–9.
19. Chen CS, Yang P, Yen CF, Wu HY. Validation of impact of events scale in nurses under threat of contagion by severe acute respiratory syndrome. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. (2005) 59:135–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.2005.01347.x
20. Cheng SKW, Wong CW, Tsang J, Wong KC. Psychological distress and negative appraisals in survivors of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Psychol Med. (2004) 34:1187–95. doi: 10.1017/S0033291704002272
21. Koh D, Lim M, Chia S, Ko S. Risk perception and impact of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) on work and personal lives of healthcare workers in Singapore: what can we learn? Med Care. (2005) 43:676–82. doi: 10.1097/01.mlr.0000167181.36730.cc
22. Hong X, Currier GW, Zhao X, Jiang Y, Zhou W, Wei J. Posttraumatic stress disorder in convalescent severe acute respiratory syndrome patients: a 4-year follow-up study. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. (2009) 31:546–54. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2009.06.008
23. Mak IWC, Chu CM, Pan PC, Yiu MGC, Chan VL. Long-term psychiatric morbidities among SARS survivors. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. (2009) 31:318–26. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2009.03.001
24. Nicastri E, Balestra PRM. Temporary neurocognitive impairment with Ebola virus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2016) 87:1386–7. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2016-313695
25. Styra R, Hawryluck L, Robinson S, Kasapinovic S, Fones C, Gold WL. Impact on health care workers employed in high-risk areas during the Toronto SARS outbreak. J Psychosom Res. (2008) 64:177–83. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2007.07.015
26. Wang Y, Xu B, Zhao G, Cao R, He X, Fu S. Is quarantine related to immediate negative psychological consequences during the 2009 H1N1 epidemic? Gen Hosp Psychiatry. (2011) 33:75–7. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2010.11.001
27. Wu KK, Chan SK, Ma TM. Posttraumatic stress after SARS. Emerg Infect Dis. (2005) 11:1297–300. doi: 10.3201/eid1108.041083
28. RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R., Boston, MA: RStudio, Inc. (2015). Available online at: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed August 1, 2020).
30. Powell C. CGPfunctions: Powell Miscellaneous Functions for Teaching and Learning Statistics. R package version 0.6.0 (2020). Available online at: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=CGPfunctions (accessed August 1, 2020).
31. Brooks SK, Webster RK, Smith LE, Woodland L, Wessely S, Greenberg N. The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: rapid review of the evidence. Lancet. (2020) 395:912–20. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30460-8
32. John N, Casey SE, Carino G, McGovern T. Lessons never learned: crisis and gender-based violence. Dev World Bioethics. (2020) 20:65–68. doi: 10.1111/dewb.12261
33. Lai J, Ma S, Wang Y, Cai Z, Hu J, Wei N. Factors associated with mental health outcomes among health care workers exposed to coronavirus disease 2019. JAMA Netw Open. (2020) 3:e203976. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.3976
34. Sands N, Elsom S, Corbett R, Keppich-Arnold S, Prematunga R, Berk M, et al. Predictors for clinical deterioration of mental state in patients assessed by telephone-based mental health triage. Int J Ment Health Nurs. (2017) 26:226–37. doi: 10.1111/inm.12267
35. Al Gasseer N, Dresden E, Keeney GB, Warren N. Status of women and infants in complex humanitarian emergencies. J Midwifery Womens Health. (2004) 49:7–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jmwh.2004.05.001
36. World Bank Country and Lending Groups. The World Bank. Available online at: https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups (accessed August 1, 2020).
37. Vindegaard N, Benros ME. COVID-19 pandemic and mental health consequences: systematic review of the current evidence. Brain Behav Immun. (2020) 89:531–42. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.048



